Esports organizations are more than just teams; they’re complex businesses navigating the exciting and rapidly evolving world of competitive gaming. From securing sponsorships to managing player contracts, these organizations face unique challenges and opportunities. This exploration dives into the structures, finances, player development, marketing strategies, and legal considerations that shape the success (or failure!) of these high-stakes enterprises.
We’ll cover everything from the different organizational structures—hierarchical, flat, or hybrid—to the diverse revenue streams that fuel these operations, including sponsorships, merchandise sales, media rights, and prize money. We’ll also examine player management, brand building, and the crucial role of technology in enhancing performance and fan engagement. Think of it as a behind-the-scenes look at the business of esports, revealing the strategies and decisions that determine which organizations rise to the top.
Esports Organization Structures and Models
The esports industry, while still relatively young, boasts a diverse range of organizational structures and ownership models. Understanding these different approaches is crucial for comprehending the success (or failure) of various teams and leagues. The structure a team adopts heavily influences its operational efficiency, ability to attract talent, and ultimately, its competitive performance.
Common Organizational Structures of Esports Teams
Esports team structures, much like traditional sports, range from highly hierarchical to relatively flat. Hierarchical structures, common in larger organizations, feature clear lines of authority with a defined chain of command. This often involves distinct departments (e.g., management, coaching, marketing) reporting to a CEO or similar figure. Flatter structures, more prevalent in smaller teams, emphasize collaboration and shared decision-making.
A hybrid model, combining elements of both, is also frequently observed, particularly as teams grow and their needs become more complex. For example, a smaller team might have a flat structure for day-to-day operations but a more hierarchical structure when dealing with major sponsorships or strategic partnerships.
Ownership Models for Esports Organizations
Several ownership models exist within the esports landscape. Single ownership is a common structure, where a single individual or entity owns and controls the team. This model offers greater control and decision-making power but also carries greater personal financial risk. Investor-backed organizations involve multiple investors providing capital in exchange for equity. This can provide substantial funding for growth but may also dilute the owner’s control and introduce conflicting priorities.
Publicly traded esports organizations, while less common currently, offer the potential for significant capital raising but also subject the organization to greater public scrutiny and regulatory requirements. Team Liquid, for example, has seen significant investment from a variety of sources, showcasing a successful investor-backed model.
Operational Structures of Large and Small Esports Organizations
Large esports organizations, like Cloud9 or FaZe Clan, typically have dedicated departments for various functions including player management, coaching staff, marketing, sponsorships, content creation, and administration. They often employ specialized personnel with extensive experience in each area. Smaller organizations, conversely, often have individuals wearing multiple hats, with one person handling player management, social media, and even some aspects of sponsorship acquisition.
This difference in scale significantly impacts resource allocation, operational efficiency, and the overall level of professionalism. A larger organization can afford to invest in advanced analytics and data-driven decision-making, while a smaller team might rely on intuition and a more hands-on approach.
Hypothetical Organizational Chart for a Successful Esports Team
The following organizational chart illustrates a potential structure for a successful esports team:
| Role | Responsibilities | Reports To |
|---|---|---|
| CEO | Overall strategic direction, financial oversight, stakeholder relations | Board of Directors (if applicable) |
| Head Coach | Player development, in-game strategy, team performance | CEO |
| Team Manager | Player contracts, logistics, travel arrangements | CEO |
| Marketing Manager | Brand building, sponsorships, social media management | CEO |
| Analyst | Data analysis, opponent scouting, strategic insights | Head Coach |
| Content Creator | Video production, social media content, community engagement | Marketing Manager |
This is a simplified example; a real-world organization might have additional roles and a more complex reporting structure. The key is to establish clear roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines to ensure effective communication and efficient operations.
Revenue Streams and Financial Models
Esports organizations, like any business, need diverse and robust revenue streams to thrive. Their financial models are complex, balancing high-risk investments in players and infrastructure with the potential for significant returns from sponsorships, media deals, and merchandise sales. Understanding these revenue streams and the associated budgeting processes is crucial for long-term success in this competitive industry.
Diverse Revenue Streams for Esports Organizations
Esports organizations generate revenue from a variety of sources. These streams can be broadly categorized, and their relative importance varies depending on the organization’s size, brand recognition, and the games they compete in. A successful organization will often cultivate multiple revenue streams to mitigate risk and maximize profitability.
Sponsorships
Sponsorships are a cornerstone of esports revenue. Major brands recognize the value of reaching the highly engaged and demographically desirable esports audience. Sponsorships can range from jersey patches and in-game advertising to exclusive deals integrating the sponsor’s product into team content and social media campaigns. For example, energy drink companies and gaming hardware manufacturers are frequently seen sponsoring esports teams.
The value of a sponsorship deal depends on factors such as team performance, audience reach, and the length of the contract.
Merchandise Sales
Merchandise sales provide a direct revenue stream, allowing organizations to monetize their brand and connect with fans on a personal level. This can include jerseys, hats, hoodies, and other apparel featuring team logos and player names. Successful merchandise strategies often leverage limited-edition items or collaborations with other brands to drive sales. Popular teams with strong fan bases can generate substantial revenue through their online stores and partnerships with retailers.
Media Rights
Media rights represent a significant revenue opportunity, especially for organizations with popular teams and leagues. This includes broadcasting rights for tournaments and matches, which can be sold to streaming platforms or television networks. The value of media rights is directly tied to viewership numbers and the popularity of the game. Organizations may also generate revenue through content creation and distribution on their own channels, such as YouTube or Twitch.
Prize Money
While prize money is often associated with player earnings, it can indirectly contribute to the organization’s financial success. Winning tournaments generates positive publicity, attracts sponsors, and boosts merchandise sales. This indirect revenue generation makes strong tournament performance a crucial aspect of the organization’s overall financial health.
Budgeting Process for an Esports Organization
Effective budgeting is vital for the financial stability of an esports organization. The budgeting process involves forecasting revenue and expenses, allocating resources strategically, and tracking performance against the budget. Key expense categories include:
Key Expense Categories
- Player Salaries and Benefits: This is often the largest expense, reflecting the importance of skilled players to team success. Contracts can vary significantly based on player skill, experience, and market demand.
- Coaching Staff and Support Personnel: A strong support team, including coaches, analysts, and managers, is essential for player development and team performance. Salaries and benefits for these individuals represent a significant expense.
- Travel and Accommodation: Travel expenses for tournaments and events can be substantial, especially for international competitions.
- Equipment and Infrastructure: Maintaining high-performance computers, peripherals, and training facilities is necessary for competitive play. This includes costs for upgrades, repairs, and maintenance.
- Marketing and Public Relations: Building brand awareness and engaging fans requires investment in marketing campaigns, social media management, and public relations activities.
- Legal and Administrative Expenses: These include costs for legal counsel, accounting services, and general administrative overhead.
Successful Financial Strategies
Successful esports organizations employ a range of strategies to manage their finances effectively. These include diversifying revenue streams, securing long-term sponsorships, optimizing operational efficiency, and investing in data-driven decision-making. For example, Team Liquid has shown success through a diversified approach including strong sponsorship deals and a successful merchandise business. Cloud9’s focus on content creation has expanded their reach and brand recognition, leading to greater sponsorship opportunities.
Hypothetical Financial Model
This hypothetical model projects the financial performance of a fictional esports organization, “Apex Gaming,” over a three-year period. It’s crucial to note that these are illustrative figures and actual results will vary greatly based on many factors.
| Metric | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue (USD) | 500,000 | 750,000 | 1,200,000 |
| Expenses (USD) | 400,000 | 600,000 | 900,000 |
| Profit (USD) | 100,000 | 150,000 | 300,000 |
Player Management and Development
Landing a spot on a pro esports team is the dream for many gamers, but it’s a highly competitive field. Esports organizations understand this, and successful ones invest heavily in acquiring and nurturing talent. This involves sophisticated recruitment strategies, robust player development programs, and strong support systems that help players not just perform at their peak but also thrive in the demanding world of professional gaming.Player management in esports isn’t just about finding the best players; it’s about building a team that works well together and can consistently perform at a high level.
This requires a multi-faceted approach, combining data-driven decision making with a deep understanding of the human element.
Esports Player Recruitment and Retention Strategies
Recruiting top-tier talent is crucial for any esports organization. This often involves scouting tournaments, analyzing player statistics and performance data, and networking within the gaming community. Retention, however, is equally important. Organizations employ strategies such as competitive salaries and benefits packages, opportunities for career advancement (coaching, management, streaming), and fostering a positive team environment to keep their players engaged and motivated.
Loyalty bonuses and performance-based incentives are also common practice. Building strong relationships with players, understanding their individual needs and goals, and investing in their personal well-being are also key to retention. Organizations might offer mental health resources, coaching on financial management, and opportunities for education and skill development outside of gaming.
The Role of Coaching Staff in Player Development
Coaching staff are vital in optimizing player performance and fostering team synergy. Coaches analyze gameplay footage, identify areas for improvement, and develop tailored training plans for individual players and the team as a whole. They often incorporate elements of sports psychology to address mental fortitude, stress management, and team dynamics. Beyond tactical and strategic coaching, good coaches also act as mentors, providing guidance on personal development, conflict resolution, and professional conduct.
A strong coaching staff can significantly influence a team’s success and longevity. They’re not just teaching the game; they’re building a high-performing team.
Key Factors Contributing to Successful Player Management
Several factors contribute to effective player management. Firstly, a clear organizational structure and defined roles are essential for seamless operations. Secondly, data-driven decision making, utilizing performance analytics and player statistics, allows for informed choices regarding player recruitment, development, and roster changes. Thirdly, a strong team culture emphasizing collaboration, mutual respect, and open communication is critical for player well-being and team performance.
Finally, effective communication between players, coaches, management, and support staff ensures everyone is aligned on goals and expectations. A lack of any of these factors can lead to internal conflict, decreased performance, and player attrition.
Sample Player Development Program
A well-structured player development program is crucial for maximizing player potential. This program Artikels a framework that can be adapted based on the game, player skill level, and team needs.
The following program emphasizes a holistic approach, addressing both in-game skills and the personal well-being of the players.
- Individualized Training Plans: Each player receives a personalized training schedule based on their strengths and weaknesses, focusing on specific skills like aim, decision-making, and game sense.
- Team Scrims and Practice Matches: Regular scrimmages against other teams and internal practice matches provide valuable experience and allow players to test strategies and improve teamwork.
- Performance Analysis and Feedback: Regular review of gameplay footage, with detailed feedback from coaches, helps players identify and address their performance issues.
- Mental Skills Training: Incorporating techniques like mindfulness, visualization, and stress management to enhance mental resilience and performance under pressure.
- Physical Fitness and Wellness: Encouraging healthy habits, including proper nutrition, exercise, and sufficient sleep, to optimize physical and mental health.
- Educational and Career Development Opportunities: Providing access to resources for further education, skill development in areas outside of gaming, and exploring career paths beyond professional gaming.
- Performance Metrics and Tracking: Regularly tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as KDA (Kill/Death/Assist ratio), win rate, and objective control to monitor progress and identify areas needing improvement.
- Support Systems: Access to sports psychologists, nutritionists, and other support staff to address players’ physical and mental well-being.
Brand Building and Marketing
Esports organizations face a unique challenge: building a brand that resonates with a highly engaged but fragmented audience. Success hinges on understanding the nuances of the gaming community, leveraging digital platforms effectively, and crafting a compelling narrative that goes beyond just winning tournaments. This requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing strategic partnerships, creative content marketing, and a deep understanding of the target demographic.Esports organizations utilize a variety of strategies to build their brand and engage fans.
These strategies often blend traditional marketing techniques with innovative digital approaches tailored to the online nature of esports. Effective brand building requires a consistent message, strong visual identity, and a proactive community management strategy.
Successful Marketing Campaigns
Several esports organizations have executed remarkably successful marketing campaigns. For example, Team Liquid’s partnership with various brands, like Monster Energy and Secretlab, has significantly boosted their visibility and revenue. Their campaigns often feature engaging video content showcasing players’ personalities and behind-the-scenes glimpses into team life. Similarly, FaZe Clan’s influencer marketing strategy, leveraging the popularity of its content creators across platforms like YouTube and Twitch, has helped cultivate a massive and highly engaged fanbase.
This strategy relies on authentic content that resonates with their target audience, primarily younger generations interested in gaming and lifestyle. Their campaigns frequently involve collaborations with other influencers and brands, amplifying their reach and impact.
Comparative Branding Approaches
Different esports organizations adopt distinct branding approaches. Some, like Cloud9, cultivate a professional and polished image, emphasizing their competitive success and partnerships with major sponsors. Their branding projects an image of stability and high performance. Others, like 100 Thieves, adopt a more lifestyle-oriented approach, incorporating fashion and streetwear into their brand identity, appealing to a broader audience interested in the culture surrounding esports.
This approach expands their brand reach beyond the core gaming community. The contrasting approaches highlight the diverse avenues available for building a successful esports brand. The key difference lies in the target audience and the overall brand personality each organization aims to project.
Marketing Plan for a New Esports Organization
This marketing plan targets aspiring gamers and esports enthusiasts aged 16-25, focusing on building a strong online presence and fostering community engagement.
Target Audience
The primary target audience is young adults (16-25) passionate about competitive gaming, specifically focusing on [insert specific game genre, e.g., first-person shooters]. Secondary audiences include potential sponsors and media outlets interested in the growth of the esports market.
Messaging
The core message will emphasize the organization’s commitment to competitive excellence, fostering a positive and inclusive community, and providing opportunities for both professional and amateur players. The brand will be positioned as [insert desired brand positioning, e.g., innovative, exciting, supportive]. This messaging will be consistent across all platforms.
Channels
The marketing strategy will leverage several channels:
- Social Media: Active engagement on platforms like Twitch, YouTube, Twitter, and Instagram. Regular updates, behind-the-scenes content, and interactive community features will be employed.
- Livestreaming: Regular live streams of practices and matches on Twitch, with interactive Q&A sessions with players and coaches.
- Website: A user-friendly website providing information on the team, players, sponsors, and upcoming events.
- Public Relations: Securing media coverage in relevant gaming publications and news outlets.
- Influencer Marketing: Collaborating with relevant gaming influencers to promote the organization and its events.
Esports Organization Partnerships and Sponsorships
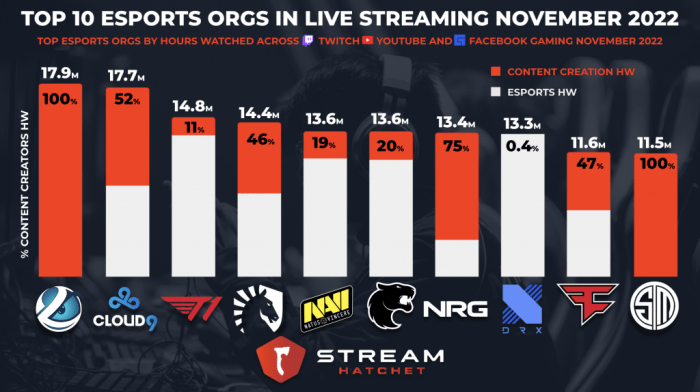
Securing sponsorships is crucial for esports organizations’ financial stability and growth. These partnerships provide vital funding, allowing teams to invest in player salaries, infrastructure, and marketing, ultimately boosting their competitive edge and brand visibility. However, navigating the sponsorship landscape presents unique challenges, requiring careful consideration of brand alignment, contract negotiations, and performance measurement.
Benefits and Challenges of Securing Sponsorships
Successful sponsorships offer numerous benefits to esports organizations. Increased financial resources are paramount, allowing for improved player recruitment and retention, better training facilities, and enhanced content creation. Brand awareness and visibility also skyrocket, leading to increased fan engagement and merchandise sales. Sponsorships can open doors to new markets and demographics, expanding the organization’s reach and influence. However, securing these partnerships isn’t without its hurdles.
Finding brands with compatible values and target audiences requires significant effort. Negotiating favorable terms, including payment structures and performance metrics, can be complex. Maintaining positive relationships with sponsors and consistently delivering on contractual obligations is vital for long-term success. Negative publicity or controversies can severely impact sponsor relationships and jeopardize future opportunities.
Examples of Successful Partnerships
Many successful partnerships demonstrate the power of collaboration between esports organizations and brands. For example, the partnership between Red Bull and various esports teams has been highly successful, leveraging Red Bull’s association with high-performance and energy to align with the competitive nature of esports. Similarly, partnerships between gaming hardware manufacturers, like Logitech G and Razer, and esports organizations provide mutually beneficial opportunities for product promotion and brand exposure.
These partnerships often involve exclusive deals, co-branded merchandise, and integrated marketing campaigns, showcasing the potential for synergy between the two parties. Another noteworthy example is the long-standing partnership between Team Liquid and Alienware, demonstrating the sustained value of aligning a prominent esports organization with a leading technology brand.
Key Factors to Consider When Negotiating Sponsorship Deals
Several key factors must be considered when negotiating sponsorship deals. First, aligning brand values and target audiences is crucial. A mismatch can lead to ineffective campaigns and damage both brand reputations. The length of the contract and payment structure should be carefully considered, balancing immediate financial needs with long-term stability. Clear performance metrics are essential to track the success of the partnership and justify future renewals.
These metrics could include viewership numbers, social media engagement, and merchandise sales. Finally, legal aspects, including intellectual property rights and termination clauses, must be thoroughly reviewed and negotiated. Transparency and open communication are essential throughout the entire process.
Hypothetical Sponsorship Proposal: “Cloud9” and “Gatorade”
This proposal Artikels a sponsorship partnership between Cloud9, a leading North American esports organization, and Gatorade, a prominent sports drink brand. The partnership aims to leverage Cloud9’s strong fanbase and Gatorade’s association with athletic performance to create mutually beneficial marketing campaigns.
| Package | Cost | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bronze | $50,000 | Logo placement on Cloud9 jerseys during online matches, social media shout-outs, and inclusion in Cloud9’s newsletter. |
| Silver | $150,000 | All Bronze benefits, plus logo placement on Cloud9’s streaming overlays, dedicated social media campaign, and inclusion in pre- and post-game interviews. |
| Gold | $300,000 | All Silver benefits, plus exclusive content creation featuring Cloud9 players, on-site branding at major tournaments, and a co-branded merchandise line. |
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Navigating the legal landscape is crucial for any esports organization aiming for long-term success. The industry, while rapidly expanding, is still relatively young, meaning legal frameworks are constantly evolving and adapting to new challenges. Understanding these complexities is key to avoiding costly mistakes and ensuring smooth operations.Esports organizations face a unique blend of legal issues stemming from traditional sports law, intellectual property law, contract law, and even labor law.
Failure to address these concerns can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal action. Proactive legal planning is therefore essential.
Contracts and Agreements
Contracts form the bedrock of the esports industry. From player contracts outlining salaries, performance expectations, and intellectual property rights, to sponsorship agreements detailing marketing obligations and payment schedules, nearly every aspect of an organization’s operations relies on legally sound contracts. These agreements should be meticulously drafted by experienced legal counsel to protect the organization’s interests and ensure clarity for all parties involved.
Failing to do so can result in disputes, lost revenue, and damaged relationships. For example, a poorly written player contract might lead to disagreements over image rights or termination clauses, causing significant problems for both the player and the organization.
Intellectual Property Rights, Esports organizations
Intellectual property (IP) is paramount in esports. This encompasses various assets, including team logos, branding, player names and likenesses, game-specific content, and even unique strategies and gameplay recordings. Protecting these IP rights through trademarks, copyrights, and potentially patents is vital for maintaining a competitive edge and generating revenue streams. Infringement can lead to expensive legal battles and significant financial losses.
For instance, unauthorized use of a team’s logo on merchandise could result in substantial damages. Organizations must actively monitor for IP infringement and take appropriate legal action when necessary.
Potential Legal Challenges
Esports organizations face a range of potential legal challenges. These include disputes with players over contract terms, intellectual property infringement claims, sponsorship agreement breaches, and issues related to data privacy and consumer protection. The increasing use of online platforms also introduces challenges relating to cyber security and data protection regulations like GDPR. Furthermore, labor laws surrounding player classification (employee vs.
independent contractor) are constantly evolving and present complexities for organizations. A significant challenge lies in the global nature of esports, necessitating compliance with various jurisdictions’ laws and regulations. For example, a dispute involving a player from one country and an organization based in another could necessitate navigating complex international legal frameworks.
Key Questions Answered: Esports Organizations
What are the common salaries for esports players?
Player salaries vary wildly depending on the game, the organization, and the player’s skill level. Some top players earn millions, while others might receive a smaller salary supplemented by prize money and sponsorships.
How do esports organizations find new talent?
Organizations use a variety of methods, including scouting events, online tournaments, and working with player agents. They often look for raw talent, potential, and a strong work ethic.
What are some common legal issues faced by esports orgs?
Common legal issues include contract disputes with players, intellectual property rights, and navigating international regulations regarding gaming and sponsorship.
What role does data analytics play in esports?
Data analytics is increasingly important for analyzing player performance, identifying strategic weaknesses, and optimizing training regimens. It’s a key component of modern esports team management.