Team Dynamics – Team Dynamics: It’s more than just a bunch of people working together, right? This deep dive explores how teams really
-work*, from the awesome synergy of a perfectly oiled machine to the epic train wrecks of communication breakdowns. We’ll cover everything from identifying personality clashes to mastering conflict resolution, and even how to navigate the weirdness of virtual teams.
Get ready to level up your teamwork game!
We’ll examine the various stages of team development, pinpointing common challenges and offering practical strategies to overcome them. We’ll also explore how leadership styles, organizational culture, and even individual personalities impact overall team effectiveness. Think of this as your ultimate guide to building a kick-ass team.
Defining Team Dynamics
Team dynamics refer to the forces that influence the interactions and relationships within a group of people working together. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for achieving team goals and fostering a positive work environment. Effective teams leverage positive dynamics to boost productivity and morale, while struggling teams often find themselves hampered by negative interactions.Team dynamics are complex and multifaceted, shaped by a variety of factors.
However, several core components contribute significantly to their effectiveness.
Core Components of Effective Team Dynamics
Effective team dynamics are built on a foundation of trust, clear communication, shared goals, and mutual respect. Trust allows team members to feel comfortable taking risks and offering constructive criticism. Clear communication ensures everyone is on the same page and understands their roles and responsibilities. Shared goals provide a common purpose that unites the team and motivates individuals to work towards a common objective.
Finally, mutual respect fosters a collaborative environment where differences are valued and individuals feel appreciated. The absence of any of these components can significantly hinder a team’s success.
Examples of Positive and Negative Team Dynamics
Positive team dynamics are often characterized by high levels of collaboration, open communication, and mutual support. For example, a software development team might exhibit positive dynamics by regularly holding brainstorming sessions, openly sharing feedback on each other’s code, and celebrating milestones together. Conversely, negative team dynamics can manifest as conflict, lack of communication, and a feeling of isolation among team members.
Imagine a sales team where individual members compete aggressively, hoard leads, and refuse to share best practices; this is a clear example of negative dynamics impacting overall performance.
Impact of Communication Styles on Team Dynamics
Communication styles significantly influence team dynamics. Teams with members who communicate openly, actively listen, and provide constructive feedback tend to be more effective and cohesive. In contrast, teams with poor communication, such as those where individuals are passive-aggressive, avoid conflict, or dominate conversations, often struggle to achieve their goals. For instance, a team using asynchronous communication tools like Slack might encounter challenges if members don’t respond promptly or clarify ambiguities, leading to misunderstandings and delays.
Conversely, a team utilizing regular face-to-face meetings can foster stronger relationships and quicker resolution of issues.
Influence of Individual Personalities on Team Dynamics
Individual personalities play a significant role in shaping team dynamics. Teams composed of individuals with diverse personalities can be highly effective if managed well. However, personality clashes can lead to conflict and hinder progress. For example, a team with several highly assertive individuals might experience frequent disagreements and power struggles, while a team with predominantly passive individuals might struggle to make decisions efficiently.
Understanding personality types, such as those described in the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI), can help team leaders anticipate potential conflicts and develop strategies to leverage the strengths of each member. Effective team leaders can foster an inclusive environment where diverse personalities contribute positively to the team’s overall success.
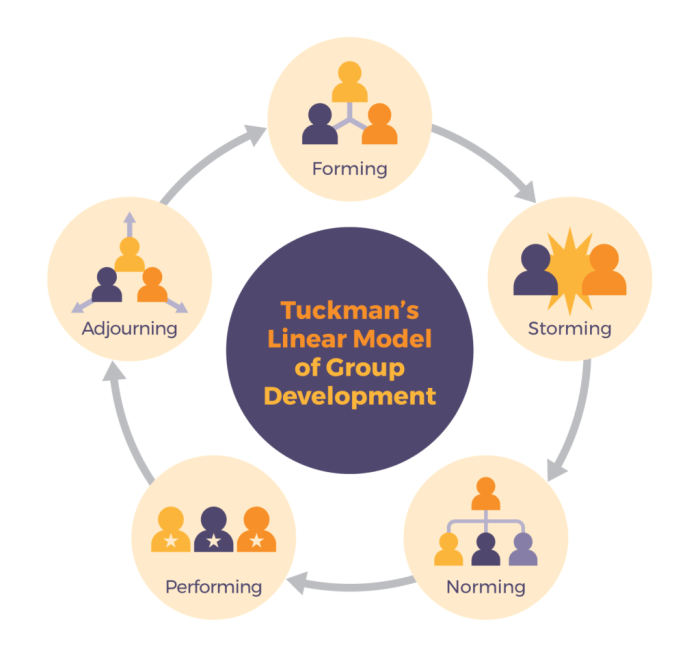
Stages of Team Development
Understanding how teams evolve is crucial for effective leadership and maximizing productivity. Team development isn’t a linear process; it’s more like a spiral, with teams potentially revisiting earlier stages as circumstances change. Knowing the typical stages and their associated challenges helps anticipate issues and proactively implement strategies for success.
Tuckman’s Stages of Team Development
Tuckman’s model is a widely recognized framework illustrating the typical stages a team progresses through. It Artikels four key phases, plus a fifth often added later: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. This model provides a useful lens through which to examine team dynamics and development.
| Stage | Characteristics | Challenges | Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forming | Members are polite and tentative, avoiding conflict. There’s a focus on getting to know each other and understanding the task. Roles and responsibilities are often unclear. | Uncertainty about roles, goals, and team dynamics. Lack of trust and cohesion. Dependency on the leader. | Clearly define roles and responsibilities. Facilitate icebreakers and team-building activities. Establish clear goals and expectations. Foster open communication. |
| Storming | Conflict arises as members assert their opinions and compete for influence. There’s a lack of agreement on processes and goals. Frustration and tension are common. | Conflict and disagreement. Power struggles. Resistance to authority. Difficulty making decisions. | Encourage open and respectful communication. Facilitate conflict resolution. Establish clear decision-making processes. Focus on shared goals and objectives. Promote active listening. |
| Norming | Members begin to cooperate and trust each other. Shared norms and expectations develop. There’s a greater sense of cohesion and team identity. | Maintaining momentum. Preventing groupthink. Addressing lingering conflicts. | Reinforce positive behaviors and team norms. Encourage participation and collaboration. Celebrate successes. Establish clear guidelines for decision-making and conflict resolution. |
| Performing | The team functions efficiently and effectively. Members are highly productive and focused on achieving goals. There’s a strong sense of shared purpose and commitment. | Maintaining motivation and engagement. Adapting to changing circumstances. Preventing burnout. | Provide regular feedback and recognition. Celebrate achievements. Offer opportunities for professional development. Encourage innovation and creativity. Delegate effectively. |
| Adjourning | The team completes its task and disbands. Members may experience a range of emotions, including sadness, relief, and pride. | Managing emotions and transitions. Ensuring a smooth handover of responsibilities. Documenting lessons learned. | Celebrate accomplishments. Facilitate a closing ceremony or debriefing session. Provide opportunities for feedback and reflection. Support members in their transition to new roles or projects. |
Facilitating Team Development Through Each Stage
A step-by-step guide to facilitate team development requires a proactive and adaptable approach. It’s about creating a supportive environment where team members feel safe to contribute, challenge, and grow. Effective facilitation involves careful observation, timely intervention, and consistent reinforcement of positive behaviors.
- Forming: Establish clear goals, roles, and expectations. Use icebreakers and team-building activities to foster trust and rapport. Encourage open communication and active listening.
- Storming: Facilitate constructive conflict resolution. Encourage open expression of opinions and perspectives. Establish clear decision-making processes. Focus on shared goals and objectives.
- Norming: Reinforce positive behaviors and team norms. Celebrate successes and milestones. Encourage participation and collaboration. Address any lingering conflicts or disagreements.
- Performing: Provide regular feedback and recognition. Delegate effectively. Encourage innovation and creativity. Offer opportunities for professional development. Adapt to changing circumstances.
- Adjourning: Celebrate accomplishments. Facilitate a closing ceremony or debriefing session. Document lessons learned. Support members in their transition to new roles or projects.
Factors Influencing Team Dynamics
Team dynamics, the interplay of personalities and interactions within a group, are significantly impacted by a variety of factors. Understanding these influences is crucial for building high-performing, collaborative teams. These factors range from individual characteristics to broader organizational contexts, all shaping how effectively a team functions and achieves its goals.
Key Factors Influencing Team Cohesion and Collaboration
Several key elements contribute to a team’s ability to stick together and work effectively. Strong leadership, clear communication, shared goals, and mutual trust are fundamental. For instance, a team with a shared vision for a project will naturally exhibit greater cohesion than one where individual members’ objectives are unclear or conflicting. Similarly, open and honest communication channels prevent misunderstandings and foster a sense of camaraderie.
Trust, built through consistent reliability and respect, allows team members to feel comfortable taking risks and relying on each other. Conversely, a lack of trust can lead to suspicion, hindering collaboration and slowing progress.
Impact of Leadership Styles on Team Dynamics
Different leadership styles profoundly impact team dynamics. Transformational leadership, characterized by inspiring vision and motivating team members, often fosters high levels of engagement and creativity. In contrast, a laissez-faire approach, while allowing for autonomy, can lead to a lack of direction and coordination. Authoritarian leadership, though effective in certain situations requiring quick decisions, may stifle creativity and individual contributions.
Democratic leadership, prioritizing collaboration and input from all members, usually results in stronger team cohesion and commitment, though it can be slower in decision-making. The optimal leadership style depends heavily on the team’s maturity, the task’s complexity, and the organizational context. For example, a startup might benefit from a transformational leader, while a well-established team might thrive under a more democratic approach.
Organizational Culture’s Effect on Team Performance and Collaboration
Organizational culture significantly influences team dynamics. A culture that values open communication, collaboration, and innovation tends to foster high-performing teams. Conversely, a culture characterized by competition, secrecy, and rigid hierarchies can hinder collaboration and lead to conflict. For example, a company with a strong emphasis on teamwork might implement collaborative tools and processes, encouraging knowledge sharing and mutual support.
In contrast, a company with a more individualistic culture might prioritize individual performance metrics, potentially leading to a less cohesive team environment. This cultural impact is pervasive, influencing everything from communication styles to the acceptance of risk and innovation within the team.
Role of Conflict Resolution in Maintaining Positive Team Dynamics
Conflict is inevitable in any team setting. However, theway* conflict is handled significantly impacts team dynamics. Effective conflict resolution strategies, focusing on addressing the underlying issues rather than personalities, are crucial for maintaining a positive and productive team environment. Ignoring conflict allows it to fester, potentially damaging team morale and productivity. Constructive conflict resolution, involving open dialogue, active listening, and a commitment to finding mutually acceptable solutions, strengthens team relationships and improves communication.
This process builds trust and demonstrates a commitment to resolving issues fairly and respectfully, ultimately enhancing the team’s overall effectiveness.
Team Roles and Responsibilities
Effective teamwork hinges on clearly defined roles and responsibilities. Without a structured approach, confusion, duplicated effort, and ultimately, project failure can easily occur. A well-defined role structure ensures everyone understands their contributions and how they fit into the larger team goal.A model for assigning roles and responsibilities should be tailored to the specific project and team size, but generally involves a combination of individual skills assessment, collaborative discussion, and formal documentation.
This process should be transparent and inclusive, allowing team members to voice their preferences and contribute to the overall structure.
Role Assignment Model
A successful role assignment model incorporates several key steps. First, a thorough assessment of each team member’s skills and experience is crucial. This might involve self-assessments, peer reviews, or even skills testing. Next, the project’s requirements are broken down into specific tasks and responsibilities. Then, based on the skills assessment, team members are assigned roles that best match their abilities and interests.
Finally, all roles and responsibilities are clearly documented, perhaps in a shared document or project management software, ensuring everyone is on the same page. Regular review and adjustment of roles based on project progress are also vital.
Importance of Clearly Defined Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly defined roles prevent overlap and gaps in responsibility. Each team member knows exactly what they are accountable for, reducing confusion and conflict. This clarity fosters individual ownership and increases efficiency, leading to improved project outcomes and a more positive team dynamic. Without this clarity, individuals might hesitate to take action, fearing they are stepping on someone else’s toes, or tasks might be neglected because no one feels solely responsible.
A well-defined structure encourages proactive behavior and a sense of shared purpose.
Examples of Team Roles and Their Functions
Several common team roles exist, each with specific functions. For example, a Project Manager is responsible for planning, organizing, and overseeing the entire project. The Team Leader facilitates communication and collaboration among team members, ensuring everyone works together effectively. Technical Specialists contribute their expertise in specific areas, such as coding, design, or research. A Communications Manager handles external and internal communication, ensuring information is disseminated effectively.
Finally, a Quality Assurance Specialist is responsible for ensuring the quality and accuracy of the team’s work. The specific roles needed will vary based on the project.
Benefits of Role Flexibility and Adaptability
While clearly defined roles are essential, maintaining some flexibility is equally important. Unexpected challenges arise in every project, and the ability to adapt roles and responsibilities as needed is key to navigating these challenges successfully. Role flexibility fosters collaboration and a willingness to help teammates, strengthening team cohesion and improving overall performance. For example, if a team member is unexpectedly unavailable, others can step in and cover their responsibilities, ensuring project continuity.
This adaptability also helps team members develop new skills and broaden their experience.
Team Dynamics in Different Contexts

Team dynamics, the interplay of personalities, roles, and communication styles within a group, are significantly shaped by the context in which the team operates. Understanding these contextual influences is crucial for effective team management and achieving optimal performance. Variations in team structure, communication methods, and the nature of the work itself profoundly impact how teams function and interact.
Virtual versus In-Person Teams
Virtual teams, relying heavily on technology for communication and collaboration, present unique challenges compared to in-person teams. In-person teams benefit from spontaneous interactions, non-verbal cues, and a shared physical space fostering stronger bonds and quicker problem-solving. Conversely, virtual teams often struggle with communication barriers, a lack of informal interaction, and difficulties in building trust and rapport. Successfully managing a virtual team requires proactive strategies to enhance communication, build relationships, and establish clear expectations.
For example, regularly scheduled video conferences, utilizing project management software, and fostering informal online communication channels can mitigate the challenges of distance. Conversely, in-person teams might face challenges related to geographical limitations, scheduling conflicts, and potential interpersonal conflicts stemming from prolonged close proximity.
Challenges and Opportunities of Managing Diverse Teams
Diverse teams, comprised of individuals with varying backgrounds, experiences, and perspectives, offer significant opportunities for innovation and creativity. However, managing these teams requires careful consideration of potential challenges. Differences in communication styles, cultural norms, and work approaches can lead to misunderstandings, conflicts, and reduced efficiency if not proactively addressed. Effective strategies for managing diverse teams include establishing clear communication protocols, promoting inclusivity and respect, and leveraging the unique strengths and perspectives of each team member.
For instance, a team with members from different cultural backgrounds might benefit from using translation tools and employing culturally sensitive communication strategies. Conversely, a team lacking diversity might miss out on valuable perspectives and approaches to problem-solving.
Team Dynamics Across Industries and Organizational Structures
Team dynamics vary significantly across different industries and organizational structures. In fast-paced, high-growth industries like technology, teams may prioritize agility and rapid iteration, often adopting flatter organizational structures and embracing flexible working arrangements. Conversely, more traditional industries with hierarchical structures might emphasize established processes and formal communication channels, leading to slower decision-making and less adaptability. The nature of the work also plays a crucial role.
Teams in creative industries might prioritize collaboration and brainstorming, while teams in manufacturing might focus on efficiency and precision. Understanding these industry-specific dynamics is crucial for tailoring team management strategies and optimizing performance. For example, a marketing team might utilize agile methodologies, while a manufacturing team might rely on lean principles.
Optimizing Team Dynamics in High-Pressure or Crisis Situations
High-pressure situations or crises demand effective team dynamics to ensure successful outcomes. Clear communication, decisive leadership, and a shared understanding of roles and responsibilities are paramount. Maintaining open communication channels, providing regular updates, and actively addressing stress and anxiety are crucial for maintaining team cohesion and performance. For example, during a product launch crisis, a strong leader can guide the team, ensuring everyone understands their roles and the overarching goals, while open communication channels allow for rapid problem-solving and adaptation.
In contrast, a lack of clear communication and leadership can lead to confusion, conflict, and ultimately, failure.
FAQ Insights
What’s the difference between a group and a team?
A group is simply a collection of individuals. A team, however, is a group working together toward a common goal with shared responsibility and accountability.
How can I identify my team’s strengths and weaknesses?
Use team assessments, 360-degree feedback, and regular team meetings to identify areas where your team excels and areas needing improvement.
What are some quick team-building activities?
Try quick icebreakers, collaborative problem-solving exercises, or even a shared lunch to foster camaraderie.
How do I handle a team member who’s consistently underperforming?
Address the issue privately, providing constructive feedback and support. If the problem persists, involve HR or management.
How can I improve communication within my team?
Establish clear communication channels, encourage open dialogue, actively listen, and provide regular feedback.
